how do we see color physics
White light from the Sun is a mixture of colours each with a different frequency. We can perceive colors in things like crayons and flowers since they reflect and absorb the rays of light.
![]()
Optics Color Icon Light Physics Branch Optometry Vector Image
7 rows Color is a function of the human visual system and is not an intrinsic property.

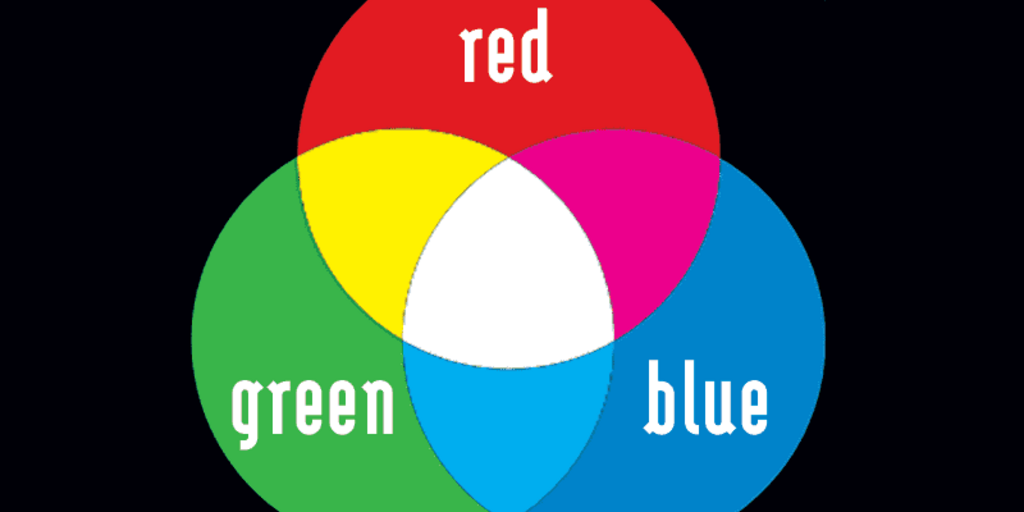
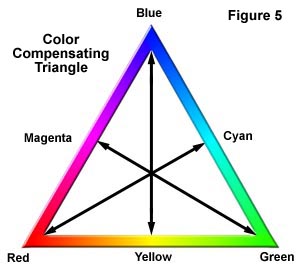
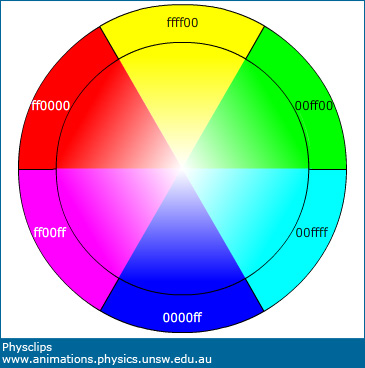
. Cone cells come in three types red light blue light and green light and they not only help us to see red blue. Sunlight reaches Earths atmosphere and is scattered in all directions by all the gases and particles in the air. Light in these colours can be added together to make the secondary colours magenta cyan and yellow.
In this first installment of a series on light Colm Kelleher describes the physics behind colors-- why the colors we see are related to the. A type of photoreceptor cell in the retina which helps us to see different colors. These light receptors are.
The physics of color perception involves energy wavelengths reflections and signals zapping back and forth in our brains. What are light and colour. A green object reflects green light.
I am not at all an expert in the biophysics of the eye but my guess is the following. For the violet line I. When you see objects you just receives light reflected or refracted from those objects which is perceived by your eye as color.
Red green and blue. A blue object reflects blue light but absorbs all other waves. The sensitivity of the eyes receptors to a light wavelength is responsible for color vision.
Colour also spelled color the aspect of any object that may be described in terms of hue lightness and saturation. Eye contains three types cells cones redblue green these are. Blue light is scattered more than the other.
You can use a prism to split or disperse white light into a spectrum of colours. The violet line leads to three readings on the red green and blue cones. The Short Answer.
Light receptors are present in the eye which transmits the messages to the brain. Rod cells help us with night vision motion detection and peripheral vision. In physics colour is associated specifically with.
A type of photoreceptor cell in the retina which helps us to see in low light. The way we see colors isnt very straightforward. The human brain and the human eye cooperatively translate light into color.
Have you ever wondered what color is. We see objects of different colors because light reflects. There are three primary colours in light.
Objects dont have a color they give off light that appears to be a color.
The Physics Of Light And Color Light Filtration Olympus Ls
The Physics Of Color Vision And Color Blindness What Is Color

The Physics Of Rainbows The Happy Housewife Home Schooling
Color Mixing And Colour Vision Physclips Light

The Physics Of Pink Why It Isn T In The Rainbow A Schooner Of Science

The Physics Of Colour What You See Isn T Necessarily What You Ve Got Cupola Contemporary Art
Structural Color Manoharan Lab
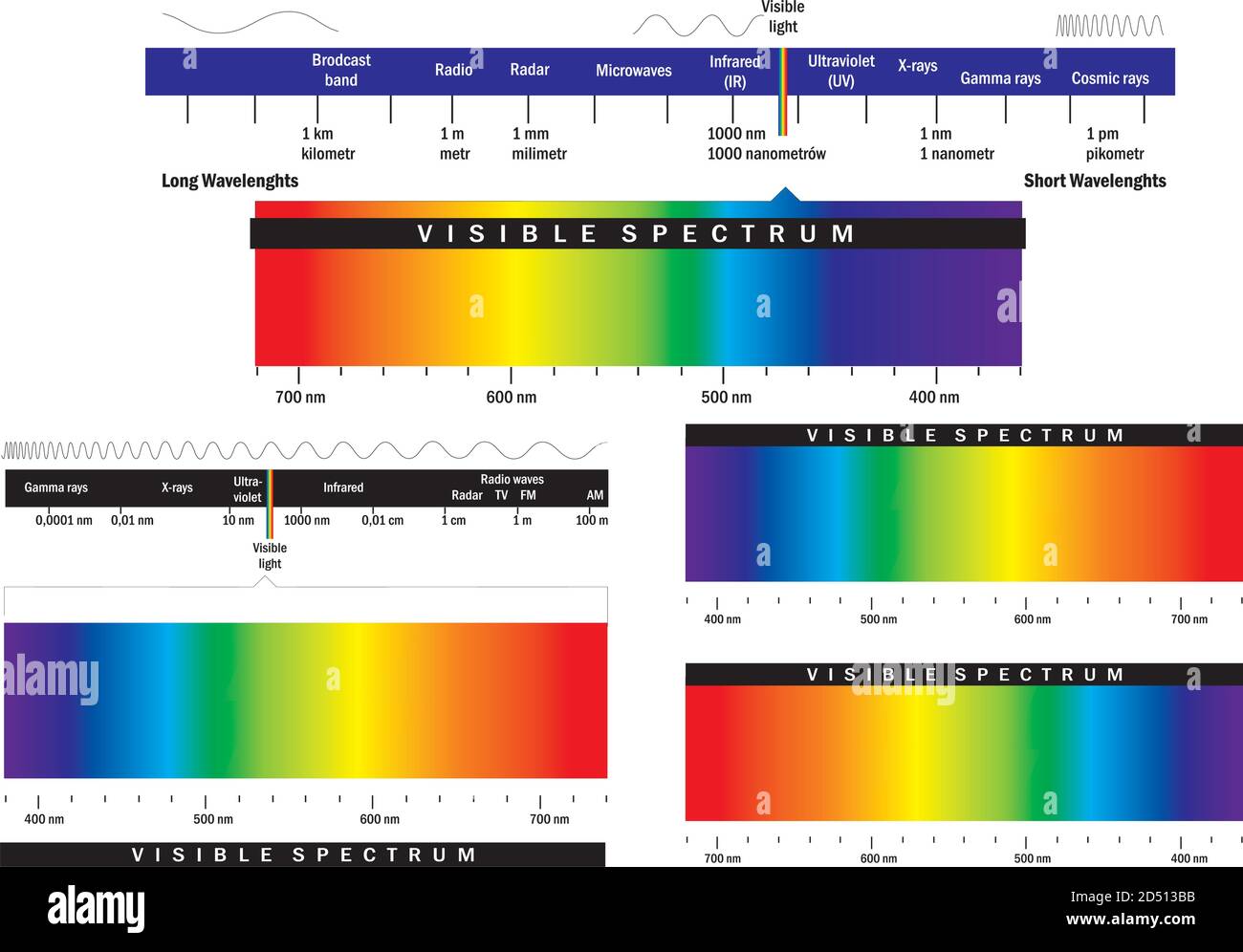
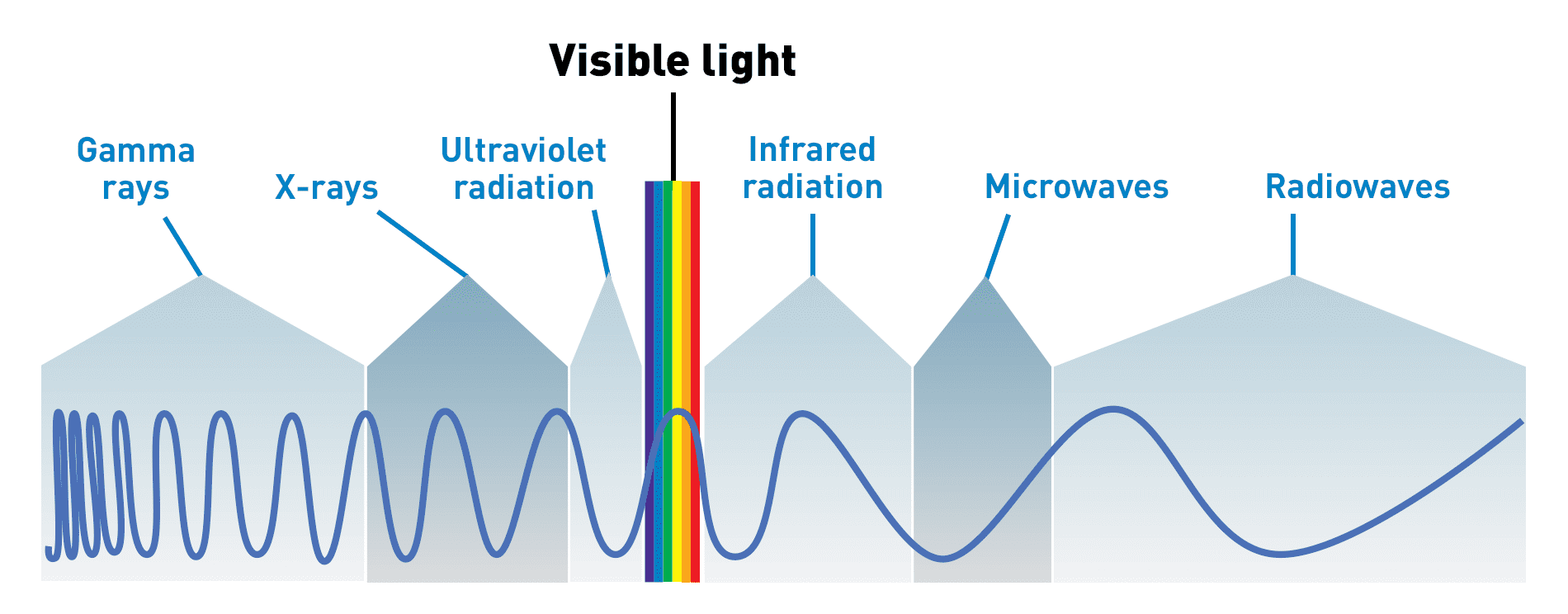
Visible Light Diagram Color Electromagnetic Spectrum Light Wave Frequency Educational School Physics Vector Background Illustration Of Spectrum Di Stock Vector Image Art Alamy
Chapter 1 The Physics Of Light And Color

Physics Light And Waves Flashcards Quizlet

How We See In Color 8th Grade Science

Premium Vector Spectrum Wavelength Visible Spectrum Color Range Educational Physics Light Line Light Wave Frequency Wavelengths Of The Visible Part Of The Spectrum For Human Eyes

Electromagnetic Radiation Which Color In Emission Spectrum Do We Really See Physics Stack Exchange

What Makes Things Coloured The Physics Behind It

Color And Color Vision Physics 101 Openstax Cnx
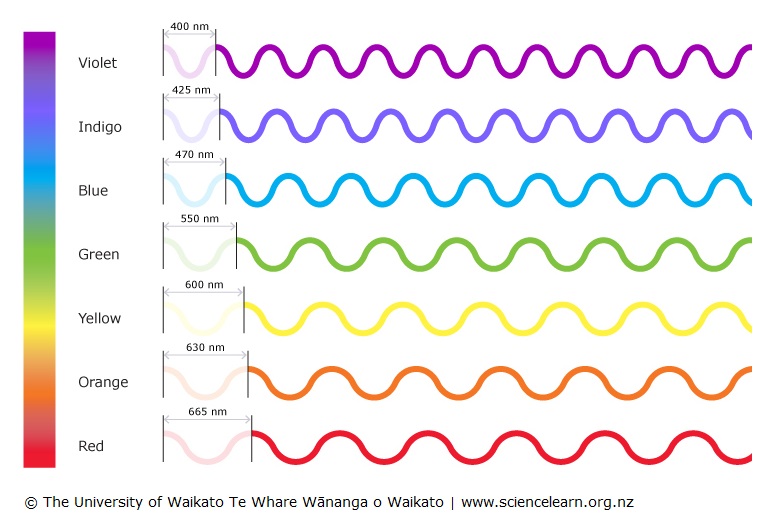
Colours Of Light Science Learning Hub

Visible Light Is White A Single Color Physics Stack Exchange